Koswara Natakusumah
(Indonesian Institute Of Science)
koswara@inkom.lipi.go.id
Abstract
MISSTI is one of information system used for science and technology (ST) data management in Indonesia. The purpose of† this system is to manage ST data and disseminate to the user through Intranet in Indonesian Institute Of† Science and Internet. The system mangos the data from Department, Non-Department, Council, Integrated Research, Society Self Fund Institution, Industry and Universities in Indonesia. This system run multi users, has completed science and technology databases, and can be accessed through Internet. Methodology used to build the system comprises: data collection, analysis, design, testing, and implementation; including building the database, data transfer, computer network, context diagram, data flow diagram, menu structure, input design, output design. In the implementation section explained the need of hardware, software, network preparation, server preparation, client preparation, database migration,† program installation, and training program.
 |
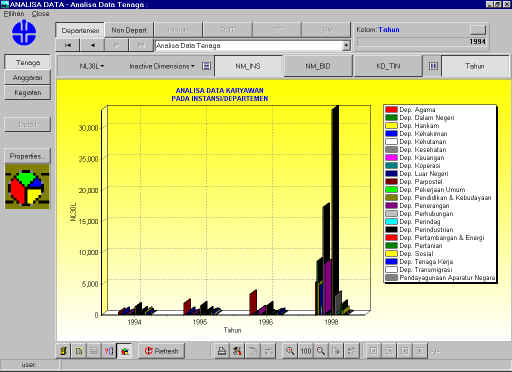
Figure 2. 22 Output design
of department manpower (bar) †
 |
 |
 |
Figure 2. 25 Output design
of non-department manpower
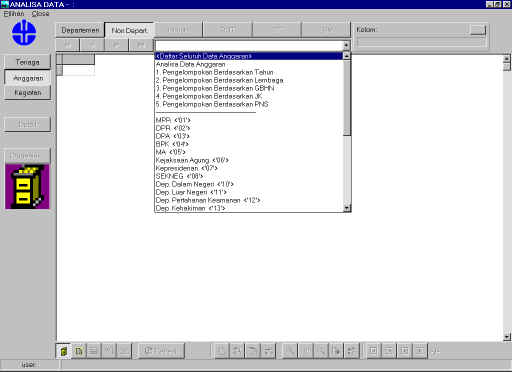 |
Figure 2. 26 Output design of non-department Finance
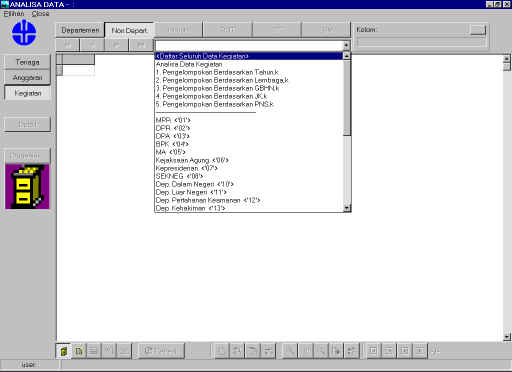 |
Figure 2. 27 Output design of non-department activities
3. Implementation
Implementation of MISSTI uses hardware, software, computer network, server installation, client installation and program installation. Hardware consists of server computer, workstation, adaptor network or network interface card (NIC), cable, and hub. Server is a central computer that manages all computer network activities, to store the data and program that can be accessed by all clients. This server runs Windows NT 4 and Microsoft SQL Server 6.5. Workstation is a computer client that can access data and program in the server computer. This client uses windows 98 to connect to the network and uses network adaptor card NE-2000. The function of this card is to have connection among computers in a network, so that all connected computers can communicate each other. To have connection among adaptor cards uses UTP cable.
Delphi 3.0 is used to build a computer program, whereas Borland database engine and ODBC are used for databases connection between client and server. The server uses operating system, database server, and driver for DBMS. Operating system uses Windows NT Verse 4.0 with Service Pack 3 or more; Database Server uses Microsoft SQL Server 6.5; and Driver for DBMS uses ODBC (available in windows NT) and BDE (Borland Database Engine). The client uses operating system and driver for DBMS. Operating system uses Windows 95/98 or newest version, whereas driver for DBMS uses ODBC and BDE.
Computer network comprises several integrated computer hardware in a network, uses certain kind of network topology and protocol that be used for computer communication. Network topology is used to manage data communication traffic, so that the network can run optimal. MISSTI uses Ethernet network architecture.† This network needs preparation of Network Card Installation for server, and network driver for ethernet card. This network needs system structure and network area for calculating how long connected cable is needed for the network, and also to manage cable lines for each workstation.
Windows NT operating system and Microsoft SQL server are installed to the computer server. This installation needs special skills of the experts, and the network administrators attend and follow the installation process in order to gain its knowledge. Microsoft SQL server 6.5 installation needs also the knowledge of how to manage the server and its SQL administration, so that the SQL server can work properly. Computer clients use Windows 95 (minimum) and in every computer client uses driver for running MIS software. There is also facility for database migration, which is carried out in the server. Before that, it prepares server and SQL administrations, and then application program for migration can be executed. The computer program is installed in the server and client. The program in the server is also prepared for the client, so that, the client can run the serverís program, but this situation† reduces capabilities of† process time and working load of the server.
4.†† Conclusion
Basic concepts of integrated system development of MISSTI is well prepared, adding new system modules can be carried out easily; and changing every modules in making reports can also be done easily, without changing source program. Databases for the future are prepared, and can be accessed through Internet. MISSTI is developed to produce different report based on userís need. Preparation of the report uses SQL (Structured Query Language) that written in a report script. Information for Internet is selected. This selection is helped by interface computer program for having good connection between MISSTI and the Internet. Up to now, MISSTI is used to manage the data for analysis and development of science and technology in Indonesia Institute of Science (see Attachment); it will develop for† the need of infrastructure Archipelagic Super-Lane 1999 in Indonesia.
Reference: 1. LIPI; A Master Plan For The R & D Management Information System, Jakarta: LIPI, 1994.
Attachment :† S&T Development Budget according to type of Expenditure and Activities in Department (DM), 1998/1999
| Department/ DM |
Fisik/Physic | Non Fisik/non-Physical | Total | ||||||
| Litbang/ R&D |
Diklat/ STE | Jasa/ STS |
Sub Total | Litbang/ R&D |
Diklat/ STE |
Jasa/ STS |
Sub Total | ||
| DPR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 37.180 | 0 | 37.180 | 37.180 |
| MA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 405.592 | 405.592 | 405.592 |
| Dalam Negeri | 20.000 | 0 | 0 | 20.00 | 848.340 | 448.325 | 1.224.903 | 2.521.568 | 2.541.568 |
| Kehakiman | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 735.029 | 0 | 701.027 | 1.436.101 | 1.436.101 |
| Keuangan | 36.560 | 0 | 3.200 | 39.760 | 960.309 | 4.610.807 | 0 | 5.571.116 | 5.610.876 |
| Pembiayaan | 0 | 0 | 398.013 | 398.013 | 2.312.205 | 0 | 14.472.353 | 16.784.558 | 17.182.571 |
| Pertanian | 338.574 | 2.310 | 1.492.200 | 1.833.084 | 21.569.076 | 6.211.536 | 6.750.009 | 34.530.621 | 36.363.705 |
| Perindag | 565.550 | 0 | 1.674.292 | 2.239.842 | 3.363.535 | 0 | 2.567.901 | 5.931.436 | 8.171.278 |
| Pertambeni | 3.835.916 | 0 | 1.108.383 | 4.944.299 | 9.993.005 | 0 | 10.137.334 | 20.130.339 | 25.074.638 |
| Pekerjaan Umum | 173.970 | 0 | 30.500 | 204.470 | 5.642.535 | 15.005.287 | 1.654.583 | 22.302.405 | 22.506.875 |
| Perhubungan | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.784.662 | 0 | 67.084 | 1.851.746 | 1.851.746 |
| P&K | 930.240 | 85.600 | 13.509.794 | 14.525.634 | 23.057.049 | 74.108.240 | 11.859.585 | 109.024.874 | 123.550.508 |
| Kesehatan | 5.483.360 | 110.259 | 110.921 | 5.704.540 | 3.109.648 | 20.561.771 | 1.742.896 | 25.414.315 | 31.118.855 |
| Agama | 188.500 | 0 | 4.055.768 | 4.244.268 | 2.555.681 | 41.326.088 | 510.966 | 4.392.765 | 48.637.033 |
| Tenaga Kerja | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.874.944 | 0 | 0 | 1.874.944 | 1.874.944 |
| Koperasi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 865.368 | 0 | 0 | 865.368 | 865.368 |
| Kehutanan | 49.722 | 0 | 0 | 49.722 | 2.852.568 | 0 | 504.291 | 3.356.859 | 3.406.581 |
| Parpostel | 0 | 0 | 457.476 | 457.476 | 1.425.721 | 208.230 | 435.984 | 2.069.935 | 2.527.411 |
| Total | 11.622.392 | 198.169 | 22.840.547 | 34.661.108 | 82.949.675 | 162.517.464 | 53.034.583 | 298.501.722 | 33.162.830 |
Source: Document DIP, processed by Papiptek-LIPI
S&T Development budget according to type of Expenditure and Activities in Non Departmental Government Institutions (NDGI), 1998/1999†††††††† (x Rp. 1.000)
| LPND/NDGI | Fisik/Physic | Non Fisik/non Physic | Total | ||||||
| R&D | Diklat/STE | Jasa/STS | Sub Total | R&D | Diklat/STE | Jasa/STS | Sub Total | ||
| LAN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 958.827 | 0 | 228.298 | 1.187.125 | 1.187.125 |
| LAPAN | 982.316 | 0 | 912.479 | 1.894.795 | 3.778.907 | 0 | 1.300.722 | 5.079.629 | 6.974.424 |
| LSN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 171.590 | 0 | 0 | 171.590 | 171.590 |
| LIPI | 12.326.911 | 0 | 919.500 | 13.246.411 | 24.129.719 | 0 | 2.417.779 | 26.547.498 | 39.793.909 |
| BATAN | 5.036.570 | 0 | 671.300 | 5.707.870 | 10.610.804 | 349.465 | 1.354.682 | 12.314.951 | 18.022.821 |
| BAPPENAS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 591.491 | 0 | 0 | 591.491 | 591.491 |
| BPPT | 8.028.517 | 38.000 | 6.570.920 | 14.637.437 | 9.588.746 | 2.704.515 | 5.071.394 | 17.364.655 | 32.002.092 |
| BP7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 289.840 | 0 | 0 | 289.840 | 289.840 |
| BPKP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 61.518 | 0 | 0 | 61.518 | 61.518 |
| BULOG | 0 | 0 | 49.000 | 49.000 | 50.000 | 0 | 197.300 | 247.300 | 296.300 |
| BKPM | 0 | 0 | 4.070.000 | 4.070.000 | 332.616 | 0 | 221.596 | 554.212 | 4.624.212 |
| BAKOSURTANAL | 36.000 | 0 | 13,357.366 | 13.393.366 | 415.774 | 0 | 1.090.859 | 1.506.633 | 14.899.999 |
| BPS | 227.828 | 0 | 2.743.428 | 2.971.256 | 763.731 | 0 | 17.025.623 | 17.789.354 | 20.760.610 |
| ARSIPNAS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 53.899 | 0 | 337.826 | 391.725 | 391.725 |
| BPN | 0 | 0 | 8.000 | 8.000 | 424.700 | 0 | 5.983 | 430.683 | 438.683 |
| Total | 26.638.142 | 38.000 | 29.301.993 | 55.978.135 | 52.222.162 | 3.053.980 | 29.252.062 | 84.528.204 | 140.506.339 |
Source: Document DIP, processed by Papiptek-LIPI
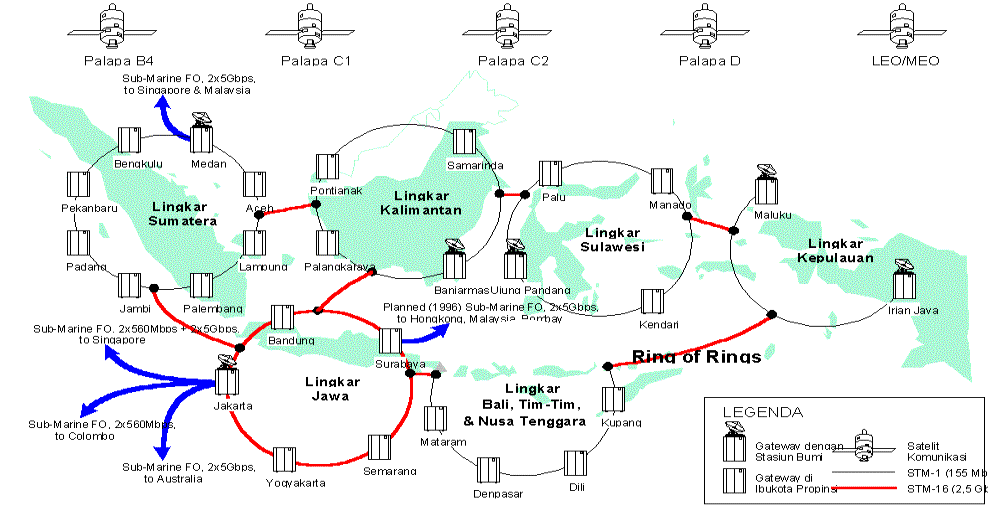 Figure
†Archipelagic Super-Lane 1999 in Indonesia
Figure
†Archipelagic Super-Lane 1999 in Indonesia
(last updated 12 July 2000)